I Need a Spell Caster That Can Help Me Cure My Herpes Disease and Get Wife Back Post Comment 2019
Introduction
The new coronavirus 2022 (COVID-19) is an epidemic in Wuhan and the population is believed to be immunologically naïve. Every bit the epidemic progresses, in that location remains trivial understanding of infant and childhood COVID-xix infections and their clinical moving picture. As of 22 February 2020, 77,043 cases of novel COVID-19 infections accept been confirmed and 2,445 people have died (http://2019ncov.chinacdc.cn/2019-nCoV/). During this epidemic, four live-born infants were born in our medical heart, to pregnant women with the COVID-xix infection. 3 of the four pregnant women gave birth by cesarean section due to concerns nigh symptomatic maternal infection. The other infant was built-in by vaginal delivery to a mother experiencing fever (highest temperature 38.3°C), with a diagnostically confirmed infection. The near important question is whether the COVID-19 could be transmitted vertically to the fetus from the pregnant mother and cause a clinically meaning infection. Recently, a finding from nine other cases suggested that there is no evidence for intrauterine infection caused by vertical transmission in women who develop COVID-19 pneumonia in late pregnancy (1). We believe this nowadays written report is the second case report on vertical transmission between COVID-nineteen pregnant women and their infants. Moreover, this written report will focus more on infants. This example report describes the clinical course of four live built-in infants born to pregnant women with the COVID-19 infection.
Case Written report
Cases of the Mothers
All four mothers were symptomatically infected with COVID-19 during the 3rd trimester. On admission, the regular symptoms of pregnant mothers with COVID-nineteen were fever (iii out of four patients), cough (2 out of four patients), myalgia or fatigue (two out of four patients), and headache (two out of four patients). Only ane patient felt reduced fetal motion and one experienced dyspnea. Lymphocytes were below the normal range (lymphocyte count <1.ane × 109/L) in all patients, and two patients showed lymphopenia (lymphocyte count <i.0 × 109/50). Both leucocytes and platelet counts were below the normal range (white blood prison cell count <4 × 10ix/50, platelet count <100 × 109/L) in the female parent in Case four (shown in Tabular array 1). The mother in Example 3 developed anemia (hemoglobin 83 g/L) and dyspnea 5 days afterward being admitted. In that location was a meaning increase of the level of C-response poly peptide in all pregnant mothers. Coagulation function and blood biochemistry of all the mothers were normal. Five respiratory pathogens (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Respiratory syncytial virus, Adenovirus, and Coxsackie virus) and the nucleic acrid of influenza viruses A and B of all patients were negative (laboratory findings shown in Table 1). An RT-PCR assay confirmed that the throat swab of the four pregnant women were positive for COVID-19. Abnormalities in breast CT images and bilateral interest were detected amidst all pregnant women. A cesarean section was performed for three patients in the astute phase of the disease while one patient underwent vaginal delivery considering of the onset of labor. Four full-term infants were built-in. All infants were isolated from their mother immediately later nascency. We draw the clinical class of these four infants (laboratory findings shown in Table 2). Three mothers of the infants recovered from their COVID-19 infections and were released three–5 days later on commitment. Nevertheless, one mother suffered severe dyspnea after delivery which required respiratory support—she did, nevertheless, survive. All four infants and their mothers were healthy upon a postal service-discharge follow-up.
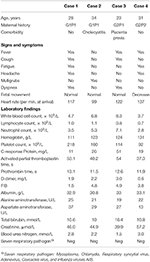
Table i. Clinic and laboratory characteristics of mothers.
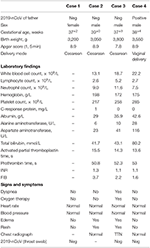
Tabular array ii. Dispensary and laboratory characteristics of the newborns.
Cases of the Infants
Three male, and one female infant was born beyond 37 weeks' gestation and had a birthweight above iii,000 g. All infants had a 1-min Apgar score of seven–viii and five-min Apgar score of 8–ix (Table 2). They were isolated from their mothers immediately after birth and received formula feeding. Three of the four infants tested negative for COVID-19 using a throat swab specimen in RT-PCR 72 h after birth and i baby'due south parents did non provide consent for their baby to be tested for COVID-19.
Two of the iv infants were good for you. Two of the four infants had rashes after nascence, even so, the rash distribution and shape differed. The baby in Case 2 had some maculopapules scattered all over the body, and ane facial peel ulceration on the forehead (size near 0.3 × 0.5 cm2). The rash disappeared and skin desquamation appeared the next solar day without any handling. The rash of the infant in Example iii was present on the forehead and seemed to diffuse minor miliary red papules on day 2. The rash disappeared on solar day 10 without handling (Table two). The infant in Instance 2, the mother of whom had cholecystitis, developed edema of the lateral thigh on day three, and the level of serum albumin was just 26 g/L. The baby was taking full formula feeds on day 4. The babe was discharged from the NICU (neonatal intensive intendance unit) 6 days subsequently nascency. The babe in Instance three, the mother of whom had placenta previa, suffered transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) and required nasal- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (nCPAP) later on birth. Breathing became regular within 3 days. The baby was taking full formula feeds on day v and was discharged from the NICU on day 7 (Tabular array two).
Discussion
In this study, 4 pregnant women were confirmed to have the COVID-xix infection. One female parent experienced reduced fetal movement. 1 mother adult anemia and dyspnea subsequently admission. Of the three infants whose parents provided consent to exist diagnostically tested, none tested positive for the virus. None of the infants developed serious clinical symptoms such equally fever, cough, or diarrhea. Two newborns had a rash, which disappeared spontaneously without handling; one newborn had mild dyspnea, and was considered to suffer from TTN and supported past not-invasive mechanical ventilation for iii days. All of the four babies are doing well and take been formula feeding since birth.
Coronavirus (CoVs) (2) is an enveloped positive-sense RNA virus, which infects humans and a wide variety of animals, causing diseases in the respiratory, enteric, hepatic, and neurological systems with varying severity (3). In the past few decades, newly evolved CoVs have posed a global threat to public health, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle Due east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) that were implicated in the 2003 outbreak in Guangdong, Communist china and the 2012 outbreak in the Centre East, respectively (2). On ten Jan 2020, a new coronavirus causing a pneumonia epidemic in Wuhan City in central China was denoted as COVID-19 by the World Health Organisation (WHO) (4). As of 22 February 2020, near 77,043 COVID-19 infections in humans accept been confirmed in People's republic of china, with at least two,445 reported deaths. As reported herein, iv pregnant women were confirmed to have the COVID-19 infection in our medical middle, which is designated as one of the handling centers for pregnant women with the COVID-19 infection. Importantly, we found neither SARS-CoV-two diagnostic positivity nor firsthand bear witness of symptomatic COVID-19 amongst the infants born to the symptomatic, test-positive mothers.
On the ground of previous reports (5–vii), SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV were associated with critical maternal illness, spontaneous ballgame, or even maternal death. In these four pregnant women with the COVID-19 infection, 3 had fever, ii had a cough and experienced headache. In laboratory data, there was lower lymphocyte count and higher CRP in blood assay. Typical CT images of COVID-19 infection with ground glass changes were presented in these meaning patients. These four pregnant women had no disquisitional maternal disease. Simply one of them experienced reduced fetal movement and one had dyspnea. These symptoms, at onset of commitment, were similar to other populations (8). To prevent COVID-nineteen intrauterine, perinatal, and postnatal transmission, iii significant women received a cesarean department. One of the three pregnant women suffered placenta previa, which made it necessary to opt for a cesarean section. But one pregnant mother adopted a vaginal delivery considering of an emergency labor procedure.
Shek et al. (9) reported that perinatal transmission of the SARS-associated coronavirus was not detected in whatever of the v live built-in infants who were built-in to significant women with SARS during the community outbreak in Hong Kong in 2003. In addition, none of the infants developed clinical, radiologic, hematologic, or biochemical bear witness suggestive of SARS. Consistent with these reports, in our study, RT-PCR assay confirmed that the throat swab of the iii cases were negative for COVID-19. We regret that the infant in Instance 2 did non have a COVID-19 diagnosis as the babe's guardian'southward did not provide consent.
Assiri et al. (7) reported 5 cases of pregnant women infected with MERS-CoV from Saudi Arabia, and all pregnancies were in the second or third trimester. Among the five pregnancies, 2 pregnant women died during their illnesses, two resulted in perinatal death (i pregnancy resulted in intrauterine fetal demise, and 1 infant died iv h later on an emergency cesarean delivery). It was reported that 12 pregnant women were diagnosed to have the SARS infection during the outbreak in Hong Kong (10). Seven mothers presented in the showtime trimester, and the rest were in their late second and tertiary trimester. It was reported that the SARS infection in significant women could lead to severe intrauterine growth retardation, which could be due to the prolonged usage of high dose systemic corticosteroids or antiviral agents and/or the affect of a astringent maternal debilitating disease on normal fetal growth (9, 10). In this study, all four cases reported on were delivered during the astute stage of the illness, at 37–39 weeks of gestation, and the nascency weight of all the babies were appropriate for their gestational age. Throughout the clinical course, there were no manifestations or radiologic, hematologic, or biochemical evidence suggestive of COVID-nineteen infection. This study is similar to reports of SARS infection (9) (Table 2).
Coronaviruses cause respiratory and intestinal infections in animals and humans (11). For adult patients, the clinical manifestations of COVID-nineteen infection include fever, cough, shortness of breath, musculus ache, sore throat, diarrhea, and so on (11). The minority of patients showed astringent and even fatal respiratory diseases such as astute respiratory distress syndrome. Co-ordinate to imaging examination, most patients showed bilateral pneumonia, multiple mottling, or ground-glass opacity. In this study, only the baby in Instance 3 showed dyspnea and required oxygen therapy. A chest radiograph of the babe in Case 3 showed that the brightness of the left lung was slightly decreased, and the texture of the right lung was slightly blurred. His condition was relieved gradually after 3 days of nCPAP treatment.
It has been confirmed that COVID-nineteen gravely damages leucocytes, and could lead to multiple organ damage forth with the respiratory system (12). In this written report, blood assays of the three infant cases were normal, and all the blood cell counts and hemoglobin concentrations fluctuated within the normal reference range. Information technology is worth noting that both Instance 2 and Case iii presented a transient skin rash afterward birth. Whether this was attributable to the maternal inflammatory toxin effect requires farther report. At follow up, the four newborns were health and had grown on formula feeding.
This feature reveals that none of the four newborns of the mothers with COVID-19 adult COVID-19 infection. In this report, viral nucleic acrid detection using real-fourth dimension polymerase concatenation reaction (RT-PCR) remains, is taken as the standard of COVID-19 infection. A recent retrospective analysis in adults showed that the sensitivity of RT-PCR is 71% for COVID-19 infection (xiii). Therefore, the reliability of diagnostic testing should exist further evaluated, peculiarly in children. Another limitation of this report was the small number of cases, and imperfect dispensary data. No COVID-19 vertical manual was detected. Further studies for viral infection in placenta, amniotic fluid, neonatal blood, gastric fluid, and anal swab, and the viral depending receptor on children volition be detected in hereafter.
Information Availability Argument
The datasets generated for this written report are available on request to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving homo participants were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Lath of Spousal relationship Hospital, Huazhong Academy of Science & Technology. Written informed consent to participate in this report was provided by the participants' legal guardian/side by side of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(southward)' legal guardian/side by side of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or information included in this article.
Writer Contributions
YC and HP designed the report, drafted the initial manuscript, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. LW, HG, YZ, and LZ designed the data drove instruments, collected the data, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. YL designed the study, coordinated, and supervised data collection, and critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and concur to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
This written report was supported by the National Natural Scientific discipline Foundation of Communist china (81500218, 81601324, and 81300523).
Disharmonize of Interest
The authors declare that the inquiry was conducted in the absence of whatever commercial or financial relationships that could exist construed equally a potential conflict of involvement.
References
1. Chen HJ, Guo JJ, Wang C, Luo F, Yu XC, Zhang W, et al. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in ix significant women:a retrospective review of medical records. Lancet. (2020) 20:30360–3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(xx)30360-3
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
4. Yu F, Du L, Ojcius DM, Pan C, Jiang S. Measures for diagnosing and treating infections past a novel coronavirus responsible for a pneumonia outbreak originating in Wuhan, Cathay. Microbes Infect. (2020) 20:30025–3. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.01.003
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
7. Assiri A, Abedi GR, Al Masri Yard, Bin Saeed A, Gerber SI, Watson JT. Middle e respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection during pregnancy: a written report of 5 cases from Saudi arabia. Clin Infect Dis. (2016) 63:951–3. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw412
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
8. Huang C, Wang Y, Li Ten, Ren Fifty, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2022 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, Mainland china. Lancet. (2020) 395: 497–506. doi: x.1016/S0140-6736(xx)30183-5
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
ix. Shek CC, Ng PC, Fung GP, Cheng FW, Chan PK, Peiris MJ, et al. Infants born to mothers with severe astute respiratory syndrome. Pediatrics. (2003) 112:e254. doi: ten.1542/peds.112.4.e254
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
10. Wong SF, Chow KM, Leung TN, Ng WF, Ng TK, Shek CC, et al. Pregnancy and perinatal outcomes of women with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2004) 191:292–seven. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2003.11.019
PubMed Abstruse | CrossRef Total Text | Google Scholar
11. Bonilla-Aldana DK, Quintero-Rada M, Montoya-Posada JP, Ramirez S, Paniz-Mondolfi A, Rabaan A, et al. SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and now the 2019-novel CoV: have we investigated enough near coronaviruses? - a bibliometric analysis. Travel Med Infect Dis. (2020) 33:101566. doi: x.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101566
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
12. Chen Northward, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2022 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, People's republic of china: a descriptive study. Lancet. (2020) 395:507–13. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(xx)30211-vii
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
chamberlaincoth1990.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2020.00104/full
0 Response to "I Need a Spell Caster That Can Help Me Cure My Herpes Disease and Get Wife Back Post Comment 2019"
Post a Comment